SKELETAL STRENGTH
OSTEOSTRONG HELPS WITH OSTEOPOROSIS
Osteoporosis is a condition of the bones specific to their density. It occurs when you lose too much bone and/or make too little bone. As a result, your bones become weak and may break from a fall. About 54 million Americans have low bone mass, which means they are at increased risk for Osteoporosis. Osteoporosis actually means “porous bone.” If you look at healthy bone under a microscope, you’ll see that parts of it look like a honeycomb. If you have osteoporosis, the holes and spaces in the honeycomb are bigger than they are in healthy bone. Many people age 50 or older make a decision to have a bone density test.
In 2012, a study was published that showed that subjects had to experience at least 4.2 times their body weight in order to trigger the growth of healthy new bone tissue. At OsteoStrong, members easily experience 4 to 10 times their own bodyweight without injury or pain, triggering the development of healthy new bone tissue according to the 2012 study.

SUPPORTING DATA

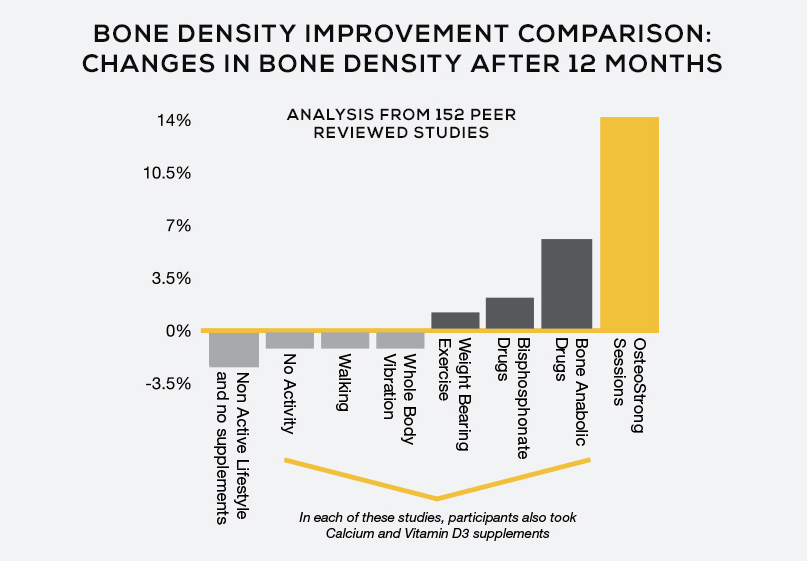
NON ACTIVE LIFESTYLE, NO SUPPLEMENTS
In 2003, the New England Journal of Medicine published an article which established that after the onset of menopause, females may lose 1.9% of their bone mass density per year.

NO ACTIVITY + CALCIUM AND VITAMIN D
A compiled analysis of 29, all randomized trials found supplementation with calcium and vitamin D was able to slow bone density loss between the hip and spine over the course of a year by half of the standard amount of loss given the other variables in an individual’s life.

WALKING + CALCIUM AND VITAMIN D
A compiled analysis of 8 studies found brisk walking type exercise showed no bone density gain between the hip and spine over the course of a year.

WHOLE BODY VIBRATION
A compiled analysis of 18 studies found whole body vibration (WBV) showed no bone density gain between the hip and spine over the course of a year, but positive implications were seen with activation of muscle, and help with balance and proper movement.

WEIGHT BEARING EXERCISE
A compiled analysis of 62 studies found weight bearing exercise showed an average of 1% bone density gain between the hip and spine over the course of a year.

BISPHOSPHONATE DRUGS + CALCIUM AND VITAMIN D
Bisphosphonate drugs like Boniva, Actonel, and Fosamax which are the standard of care can show an average of 1.6% bone density gain between the hip and spine. Side effects include increased cancer risk for those who have risk factors. Side effects include risks of abnormal bone fractures and dissolving of the human jaw. Learn more by discussing these drugs with your physician.

BONE ANABOLIC DRUGS + CALCIUM AND VITAMIN D
Forteo is a bone anabolic, which has shown an average of 6.15% bone density gain between the hip and spine. Side effects can potentially include increased cancer risk for those who have risk factors. As this drug is newer, much is still to be learned. This drug is only prescribed for patients at high risk of fracture, and patients have to be monitored closely for adverse effects. Learn more by discussing these drugs with your physician.

MUSCULOSKELETAL STRENGTH CONDITIONING
The use of osteogenic devices has shown promising results. Though there are only 4 studies on the specific application of osteogenic loading devices, the underlying principal is one of the most fundamental of human physiology (mechanotransduction as discussed earlier) and as loads seen with osteogenic use are far beyond the minimum established trigger for building bone, the results seen are beyond that of other treatments. Bone density has been shown to improve 7.34% between the spine and hip results over one year of treatment. Further, Hunte and researchers found bone density gains of over 14% after 6 months of treatment. Further research shows statistical congruency with a larger sample (n=2300) for functional bone performance gains and BMD.

